Ethylene diamine tetra acetate titration
EDTA is commonly used in the analysis of metal ions by complexation titration, called EDTA titration. It is a commonly used analytical chemistry technique that is particularly useful for determining the concentration of metal ions in solution.EDTA is a powerful chelating agent that can form stable complexes with a wide range of metal ions. Here is some basic information and steps about EDTA titration.

Content Tables
Titration principle.
- EDTA (hydrochloride or disodium salt): Select the appropriate form of EDTA, e.g. EDTA-2Na (EDTA disodium salt) is a commonly used form.
- Deionized or distilled water: for dissolving EDTA.
- Precision balance: for weighing EDTA.
- Measuring flasks or volumetric flasks: used to configure solutions.
- Stirring bar or magnetic stirrer: used to stir the solution.
- pH meter (as required): used to monitor the pH of a solution.
Configuration steps.
- Complexation reactions:
- EDTA forms stable 1:1 complexes with metal ions, so it can be used to “complex” metal ions in
solution during titrations. For example, EDTA forms complexes with calcium (Ca2+) and
magnesium (Mg2+) ions:
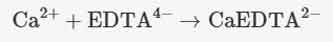
- EDTA forms stable 1:1 complexes with metal ions, so it can be used to “complex” metal ions in
solution during titrations. For example, EDTA forms complexes with calcium (Ca2+) and
magnesium (Mg2+) ions:
- Indicators:
- An indicator (e.g., Chrome Black T or ERioT) is commonly used during titrations to indicate the progress of the reaction. The indicator takes on a certain color in the presence of the metal ion and changes color when the metal ion is complexed by EDTA.
- End point of the reaction:
- The end point of a titration is when all the metal ions have reacted with EDTA and the free EDTA binds to the indicator, resulting in a noticeable change in the color of the solution.
Titration steps.
- Prepare the solution:
- A certain concentration of EDTA solution needs to be prepared and its concentration is usually calibrated with a standard metal solution before titration.
- Select the appropriate indicator:
- Select the appropriate indicator according to the metal ion to be analyzed.
- Perform titrations:
- Place the metal ion solution to be titrated in a burette and add a few drops of indicator.
- Add EDTA solution dropwise from the burette to the solution to be measured at a slow rate with continuous stirring.
- Observe the color change:
- Observe the color change of the solution until the end point of the titration is reached. Record the volume of EDTA consumed at this point.
- Calculate the concentration:
- Based on the known concentration of EDTA and the volume consumed, the concentration of the metal ion to be measured can be calculated.
Applications:
EDTA titration is widely used in the fields of water quality analysis, food monitoring, pharmaceuticals, and materials science to determine the hardness (e.g., calcium and magnesium ions) and concentration of metal ions in water.
Preautions.
- Make sure all equipment is clean before titration to avoid contamination.
- Select a suitable indicator to ensure compatibility with the metal ion to be measured.
- Vigorous stirring should be avoided during titration to avoid the introduction of air bubbles.
- Record the exact volume during the titration to ensure accurate results.
With the above steps and principles, EDTA titration has become one of the widely used techniques in analytical chemistry.
