Ethylene Diamine Tetraacetic Acid Ferric Sodium
(EDTA-FeNa)
CAS No.: 15708-41-5
Molecular Formula: C10H12N2O8FeNa.3H2O
Molecular Weight: 421.1
Structural Formula:
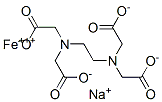
Properties:
EDTA-FeNa is used as a trace element in agriculture. It is a stable water-soluble metal chelate with oxidizability. Ferrum exists in a chelated state.
Specifications:
| Item | Index |
|---|---|
| Appearance | Brownish yellow or light yellow clean powder. |
| Chelate ferrum | ≥99% | Ferrum | ≥13.0% |
| pH value (1% aqueous solution) | 3.5-5.5 |
| Water-soluble | About 90g/L (20℃), about 120g/L (30℃), about 300g/L (70℃) |
| Bulk density: | About 650kg/m3 |
Usage:
EDTA-FeNa is used as a decoloring agent in techniques for photography. It is also an additive in the food industry. EDTA-FeNa can be the trace element in agriculture and a catalyst in the industry.
Packing and Storage:
25kg woven bag. Stored in a cool, dry place, light makes the product devitalized.
Keywords:
EDTA-FeNa; EDTA-Fe; EDTA ferrum salt.
How to prepare EDTA-Fe solution?
The Fe-EDTA solution can be prepared by dissolving Na-EDTA and FeSO4 powder in distilled water.
Taking the preparation of a 1L Fe-EDTA solution as an example: Weigh out 5.57 grams of ferrous sulfate heptahydrate, dissolve it in 80mL of distilled water. Then, heat and boil the solution, after boiling, add the pre-weighed 7.45 grams of Na2-EDTA. It is important to note that adding Na2-EDTA requires stirring while adding, and you will see a color change during the process. Next, you will be able to see the yellow chelated iron solution. Finally, cool to room temperature and transfer to a 1L volumetric flask for final volume adjustment.
Is Sodium Ferric EDTA Toxic to Human?
The EDTA-Ferric sodium provided by IRO Chelating is industrial level. So it is toxic to Humans.
-
EDTA Series
- EDTA Acid
- EDTA-Na2
- EDTA-Na4
- EDTA-CaNa2
- READ MORE...
-
Organophosphoric
- ATMP
- BHMTPMPA
- DTPMPA
- EDTMPA
- HEDP
- READ MORE...
-
Other Chelating Agent
- DTPA
- NTA.Na3
- DTPA.Na5
- READ MORE...


